Being a business owner means tracking profits, losses, annual business revenue, and more. But beyond knowing how to track these, how do you calculate the figures you need? And, how do you calculate your annual business revenue? Read on to learn the ins and outs of annual business revenue.
What is annual business revenue?
Before we dive into how to calculate annual business revenue, let’s recap what annual business revenue is. Business revenue is the grand total of your income generated by the sales of your products or services for a specific accounting period. The meaning of annual revenue is the money your business receives during the course of a year. This could mean a fiscal year (e.g., July 1 – June 30) or the calendar year (i.e., January 1 – December 31).
How does revenue differ from profits? Profit is the money you have after you account for expenses, debts, operating costs, and any additional income.
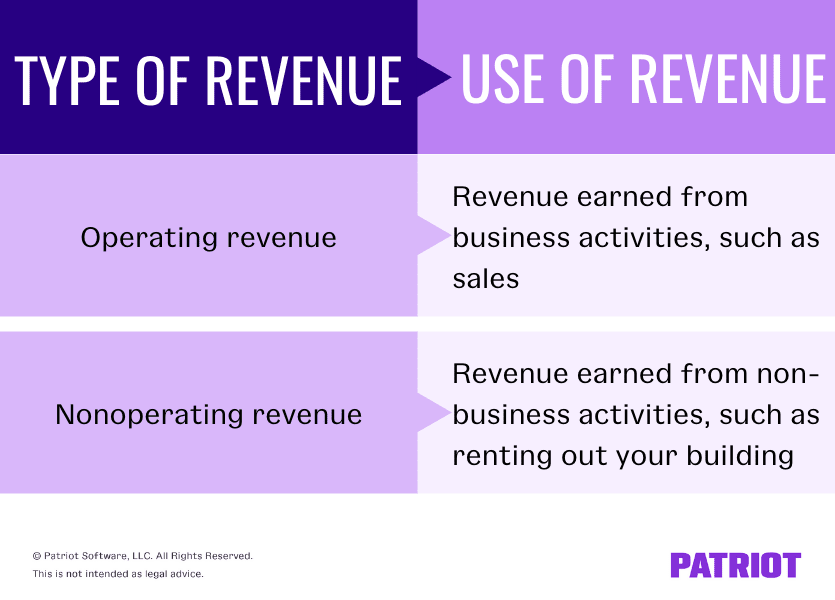
There are two types of revenue: operating and nonoperating revenue. Operating revenue is revenue you earn from your main business activities (e.g., product sales). Nonoperaating revenue is how much you earn from activities not directly related to your business (e.g., renting your building to other companies). Use both operating and nonoperating revenue to calculate your annual business revenue.
How to find annual revenue for a company
Whether you use accrual or cash-basis accounting, you can typically find your revenue on the first line of your small business income statement. The income statement is also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement. You can organize the P&L statement to show your monthly, quarterly, or annual operations.
The parts of the income statement include:
- Revenues / income
- Cost of goods sold
- Gross profit
- Expenses
- Taxes
- Net income or net loss
Keep in mind that your accounting method determines the revenue you see on your income statement:
- Accrual accounting: Include sales made on credit if you have given the goods or services to the customer
- Cash-basis accounting: Only include sales as revenue if the customer has paid you
How to calculate annual business revenue
Now that you know what revenue is and where to find it on your income statement, it’s time to learn how to calculate annual business revenue.
If you use accounting software, you can generally download an income statement report to show your annual revenue for small business. Remember that your reporting is only accurate if you enter all accounting information into the software.
To manually calculate the total annual income per product or service, use the following formula:
Revenue = Quantity of Each Product or Service X Sales Price
When you calculate the revenue for each product or service, add each total together to get your total annual business revenue (e.g., Revenue Product A + Revenue Product B).
Example 1
Say you own a bakery and sell donuts, cookie cakes, and cupcakes. You price each donut at $2.00, cookie cakes at $10.00, and cupcakes at $4.00. Last year, you sold 2,000 donuts, 1,500 cookie cakes, and 4,000 cupcakes. You do not have any investments and do not earn nonoperating revenue.
Calculate the revenue of each product by multiplying the quantity you sold of each product by its price:
Donuts: 2,000 X $2.00 = $4,000
Cookie cakes: 1,500 X $10.00 = $15,000
Cupcakes: 4,000 X $4.00 = $16,000
Your total revenue was $4,000 for donut sales, $15,000 for cookie cake sales, and $16,000 for cupcake sales.
Add together the total revenue for each product to calculate your total annual business revenue:
$4,000 + $15,000 + $16,000 = $35,000
Your total annual business revenue for the year is $35,000.
Example 2
In this example, your products and sales are the same as in Example 1. But, you own the building where you sell your products and rent out an upstairs room to another business. The business pays you $500 per month in rent.
To find your nonoperating revenue, multiply the business’s monthly rent amount by 12 months:
$500 X 12 = $6,000
You have a nonoperating revenue of $6,000. Add this total to the operating revenue from Example 1 ($35,000) to find your new annual business revenue:
$35,000 + $6,000 = $41,000
Your new annual business revenue is $41,000.
Example 3
Let’s say you offer private baking and decorating classes to your customers. Each baking class is $100, and each decorating class is $75. Last year, you hosted 300 baking classes and 400 decorating classes.
Calculate your total revenue for each class by multiplying the number of classes by the price per class:
Baking classes: 300 X $100 = $30,000
Decorating classes: 400 X $75 = $30,000
Your revenue for baking classes was $30,000, and your revenue for decorating classes was also $30,000.
Calculate the total annual business revenue by adding together the revenue for both classes:
$30,000 + $30,000 = $60,000
Your annual business revenue was $60,000.
Example 4
In this example, your business is the same as in Example 3 and has the same annual business revenue of $60,000. But, you invest some of your money and receive quarterly dividends. Each quarter, your business receives $1,000 in return on investment (ROI).
Multiply the $1,000 per quarter in ROI by the four quarters in a year to find your nonoperating revenue:
$1,000 X 4 = $4,000
Your investment resulted in a nonoperating revenue of $4,000 for the year. Add the nonoperating revenue to your operating revenue for the year from the last example to find your annual revenue:
$4,000 + $60,000 = $64,000
Your total annual revenue is $64,000.
Example 5
For this example, you own the bakery from Example 1 and provide the classes from Example 3. The prices for products and services remain the same. And, you sold the same number of baked goods and classes as in both examples.
To find your annual business revenue for both products sold and services provided, add the revenue from products and services together:
$35,000 + $60,000 = $95,000
The total annual revenue for goods sold and services is $95,000.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.