When you own a small business, it’s important to have extra cash on hand to use for investing or paying your liabilities. But with money constantly coming in and going out, it can be difficult to monitor how much is leftover. Use a retained earnings formula to track how much your business has accumulated.
Knowing the amount of retained earnings your business has can help with making decisions and obtaining financing. In this article, we will define retained earnings, explain how to calculate them, provide retained earnings examples, and explain how to record it.
What are retained earnings?
Retained earnings are business profits that can be used for investing or paying down business debts. They are cumulative earnings that represent what is leftover after you have paid expenses and dividends to your business’s shareholders or owners. Retained earnings are also known as retained capital or accumulated earnings.
You must report retained earnings at the end of each accounting period. Common accounting periods include monthly, quarterly, and yearly. You can compare your company’s retained earnings from one accounting period to another.
How to calculate retained earnings
So, what goes into retained earnings? To calculate retained earnings, you need to know your business’s previous retained earnings, net income, and dividends paid.
Learn how to calculate retained earnings below.
- Determine beginning retained earnings
You can find your business’s previous retained earnings on your business balance sheet or statement of retained earnings.
- Add net income
Your company’s net income can be found on your income statement or profit and loss statement.
- Subtract dividends paid
If you have shareholders, dividends paid is the amount that you pay them.
Retained earnings formula
Use the following retained profit formula to determine your company’s retained earnings for an accounting period:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends Paid
If you are a new business and do not have previous retained earnings, you will enter $0. And if your previous retained earnings are negative, make sure to correctly label it.
Can retained earnings be negative? If you have a net loss and low or negative beginning retained earnings, you can have negative retained earnings.
On the other hand, if you have net income and a good amount of accumulated retained earnings, you will probably have positive retained earnings.
Retained earnings examples
Let’s say that you have beginning retained earnings of $25,000. For this accounting period, you had a net income of $30,000. And, you paid dividends of $20,000.
Retained Earnings = $25,000 + $30,000 – $20,000
Retained Earnings = $35,000
You have a positive retained earnings account of $35,000.
Now, let’s look at a negative retained earnings example. You have beginning retained earnings of $4,000 and a net loss of $12,000. You did not pay dividends.
Retained Earnings = $4,000 – $12,000 – $0
Retained Earnings = -8,000
You have a deficit of $8,000 at your business. Because retained earnings are cumulative, you will need to use -$8,000 as your beginning retained earnings for the next accounting period. You will need a high net income to get out of the hole.
Retained earnings accounting
You must adjust your retained earnings account whenever you create a journal entry that raises or lowers a revenue or expense account.
Are retained earnings an asset? Retained earnings are actually reported in the equity section of the balance sheet. Although you can invest retained earnings into assets, they themselves are not assets.
Retained earnings should be recorded. Generally, you will record them on your balance sheet under the equity section. But, you can also record retained earnings on a separate financial statement known as the statement of retained earnings.
The balance sheet is split into three parts: assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. The assets section shows you the items of value that your business owns. The liabilities section shows you what you owe. And, the equity section shows you the money you have left over after paying debts.
On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear under the “Equity” section. “Retained Earnings” appears as a line item to help you determine your total business equity.
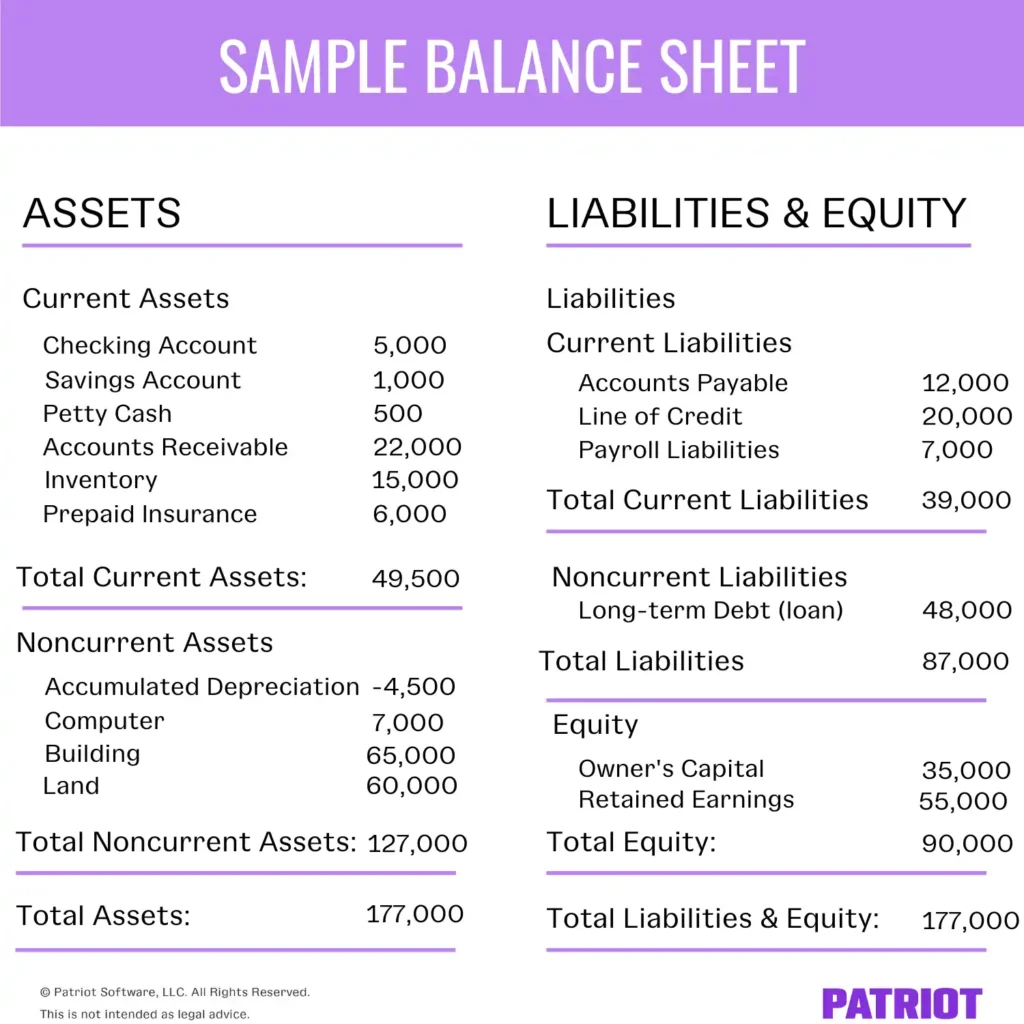
The statement of retained earnings is a financial statement entirely devoted to calculating your retained earnings. Like the retained earnings formula, the statement of retained earnings lists beginning retained earnings, net income or loss, dividends paid, and the final retained earnings.
Understanding the retained earnings formula is crucial for monitoring your business’s financial health and making informed decisions. By calculating and tracking retained earnings, you can determine how much profit is reinvested into your company or used to pay down liabilities. Whether you’re analyzing retained earnings examples to understand the concept better or learning how to define retained earnings in the context of your balance sheet, this knowledge empowers you to manage your business finances more effectively.
How do you calculate retained earnings on a balance sheet?
The retained earnings line is listed under the “Equity” section on a balance sheet. You can calculate retained earnings by using the retained earnings formula:
Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends Paid
What is included in retained earnings?
Retained earnings includes your company’s total net earnings, less any dividends paid to shareholders.
Is retained earnings the same as net profit?
Retained earnings are not the same as net profit. Retained earnings account for dividend payments to shareholders. Also, retained earnings are cumulative, whereas net profit is your company’s profit during a time period.
Ready to simplify your accounting? Patriot’s small business accounting software can help you accurately track income, expenses, and retained earnings.
This article has been updated from its original publication date of July 28, 2015.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.



